Comments Must Be Read to Enact Legislation
How a Constabulary is Fabricated
Parliament is the national legislature (law-making body) of Due south Africa. As such, one of its major functions is to laissez passer new laws, to ameliorate existing laws, and to repeal or abolish (abolish) old laws. This function is guided by the Constitution of South Africa, which governs and applies to all law and acquit inside South Africa.
Who Makes the Laws?
Both Houses of Parliament, the National Assembly (NA) and the National Quango of Provinces (NCOP), play a role in the process of making laws. A Bill or draft constabulary tin can only be introduced in Parliament by a Minister, a Deputy Government minister, a parliamentary committee, or an individual Fellow member of Parliament (MP). Nigh 90% of Bills are initiated past the Executive.
What is a Police force?
Law is a system of rules, usually enforced through a set of institutions to regulate homo conduct. It shapes politics, economics and club in many ways. There are unlike types of laws namely, contract law, holding constabulary, trust police force, criminal law, ramble law and administrative law. Constitutional law provides a framework for the creation of law, the protection of human rights and the election of political representatives. Police also raises important problems apropos equality, fairness and justice.
Did You Know?
The Apartheid legislation in Due south Africa was a chain of different laws and Acts which helped the Apartheid-government to enforce the separation of different races and consequently cement power. With the enactment of Apartheid laws in 1948, racial discrimination was legalised. One such example of discriminatory legislation was the Prohibition of Mixed Marriages Act, Act No 55 of 1949, an apartheid law which banned marriages between people of different races. This law was enforced for thirty six years and only repealed in 1985.
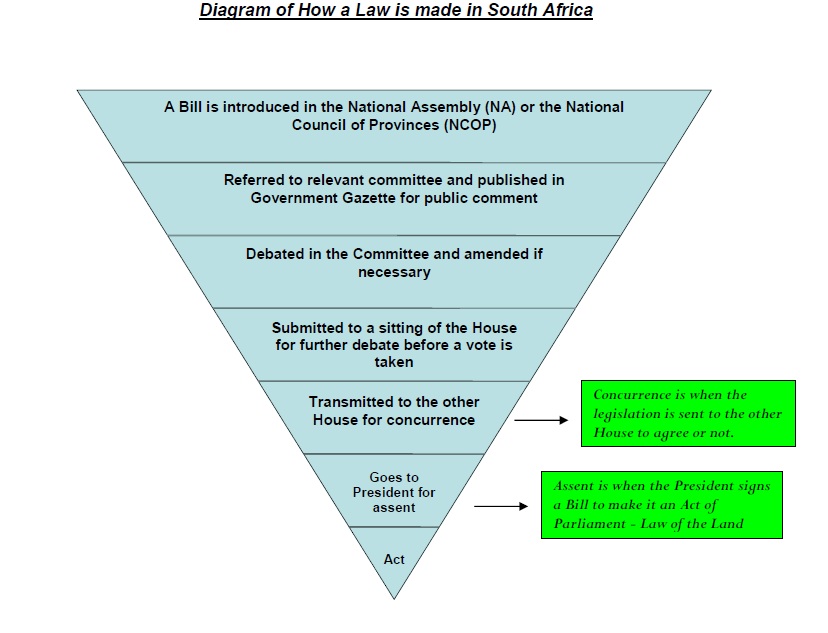
The Process of Making a Police
The process of making a law may kickoff with a discussion document called a Green Paper that is drafted in the Ministry building or department dealing with a detail upshot. This discussion certificate gives an idea of the general thinking that informs a item policy. It is then published for comment, suggestions or ideas. This leads to the development of a more refined give-and-take document, a White Paper, which is a broad statement of regime policy. Information technology is drafted by the relevant section or job team and the relevant parliamentary committees may suggest amendments or other proposals. Later on this, it is sent dorsum to the Ministry building for further give-and-take, input and final decisions.
Did You lot Know?
When a lawmaking matter is national and when information technology is provincial?
- Schedule 4 of the Constitution lists the functional areas in which Parliament and the provincial legislatures jointly have the right to make laws. This includes things like agriculture, health, housing, the environment and education (but non tertiary or higher education).
- Schedule 5 of the Constitution lists the functional areas in which simply the provincial legislatures may make laws. This includes things similar provincial roads and traffic, liquor licensing, provincial planning and provincial sport.
In exceptional circumstances Parliament may make provincial laws to maintain national security, maintain economic unity, establish minimum standards for service delivery, or to prevent unreasonable action by a province which affects the interests of another province or the land.
What is a Bill?
It is a draft version of a law. Almost Bills are fatigued up by a government department under management of the relevant minister or deputy government minister. This kind of Bill must be approved by the Cabinet before being submitted to Parliament. Bills introduced by individual Members are called Private Members' Legislative Proposals.
Did You Know?
- The Country Law Advisors certify a Neb as being consistent with the Constitution and properly drafted.
- Before a Pecker can get a law, information technology must exist considered by both Houses of Parliament (National Associates and National Council of Provinces). It is published in the Government Gazette for public comment and so referred to the relevant committee. Information technology is debated in the relevant committees of Parliament and amended if necessary. If the Bill passes through both the NA and the NCOP, it goes to the President for assent (signed into constabulary). In one case it is signed by the President, it becomes an Act of Parliament and a law of the land.
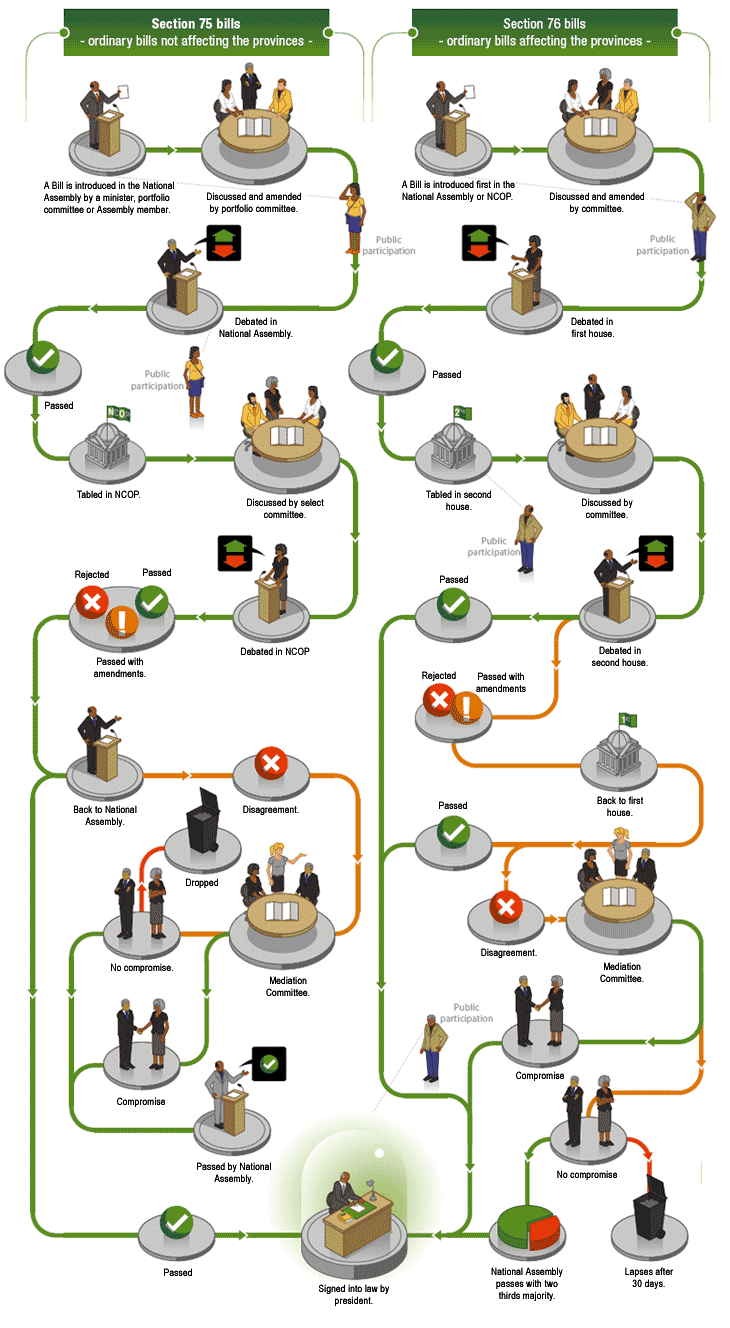
Types of Bills
Section 74 Bills deal with Constitutional Amendments (Bills amending the Constitution)
- Amending the Nib of Rights requires a vote of ii-thirds of the NA and the back up of six provinces in the NCOP. Amendments must be passed by the NCOP. All amendments affecting the provinces must be passed past both Houses.
Section 75 Bills are ordinary Bills not affecting provinces
- These Bills tin can only be introduced in the NA and in one case it is passed it is sent to the NCOP for concurrence. A Bill is passed when at that place is a majority vote by delegates present, in favour of the Beak.
Department 76 Bills are ordinary Bills that bear upon provinces
- The Bills are introduced in either the NA or NCOP and must be considered by both Houses. In the NCOP, votes are by provincial delegations and at least five provinces should vote in favour of a Bill before it is agreed to. Bills are usually considered by a provincial commission, which may hold public hearings on the Bill for comments and suggestions.
Department 77 Bills are money Bills (i.e. appropriations, taxes, levies or duties)
- Coin Bills allocate public money for a item purpose or imposes taxes, levies and duties. They tin can only be introduced by the Minister of Finance in the National Assembly. In terms of the Money Bills Amendment Procedure and Related Matters Human action, 2009 (Act No 9 of 2009), Parliament may improve money bills. 4 Act Goes to President for assent Transmitted to the other House for concurrence Submitted to a sitting of the House for further debate before a vote is taken Debated in the Committee and amended if necessary Referred to relevant committee and published in Government Gazette for public comment A Bill is introduced in the National Assembly (NA) or the National Council of Provinces (NCOP) Each blazon of Bill has a different passage to becoming a law and usually fits into but one category. If a Bill does not clearly fit onto one category, it is usually redrafted or split up into more than one Bill.
So What is Tagging?
Every bit before long every bit a Bill is introduced in Parliament it needs to exist classified into one of the 4 categories mentioned above by the Joint Tagging Mechanism (JTM). This is called "tagging" and will determine the procedures the Bill must follow to become police. The JTM consists of the Speaker and Deputy Speaker, and the Chairperson and permanent Deputy Chairperson of the Council. These office-bearers are assisted past the parliamentary legal advisors.
Source: https://www.parliament.gov.za/how-law-made
0 Response to "Comments Must Be Read to Enact Legislation"
Post a Comment